Wellbutrin, also known as bupropion, primarily works by inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. This means it increases the availability of these neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft, enhancing their effects.
Dopamine’s Role
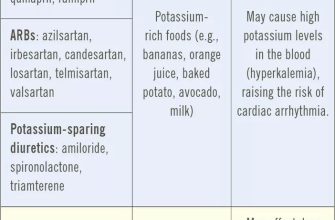
Increased dopamine levels are associated with improved mood, motivation, and focus. This is why Wellbutrin is often prescribed for depression. It’s important to note that Wellbutrin doesn’t significantly affect serotonin levels, unlike many other antidepressants.
Norepinephrine’s Influence
The impact of increased norepinephrine contributes to alertness, energy, and cognitive function. This explains why some individuals experience improved concentration and reduced fatigue while taking Wellbutrin.
Lack of Serotonin Influence and Implications
The absence of a significant effect on serotonin distinguishes Wellbutrin from many other antidepressants. This difference can be relevant for individuals who experience side effects from serotonin-affecting medications.
Further Research and Considerations
While the dopamine and norepinephrine mechanisms are well-established, research continues to explore other potential actions of bupropion within the brain.
| Dopamine | Increased availability | Improved mood, motivation, focus |
| Norepinephrine | Increased availability | Increased alertness, energy, cognitive function |
| Serotonin | Minimal effect | Reduced risk of certain side effects |