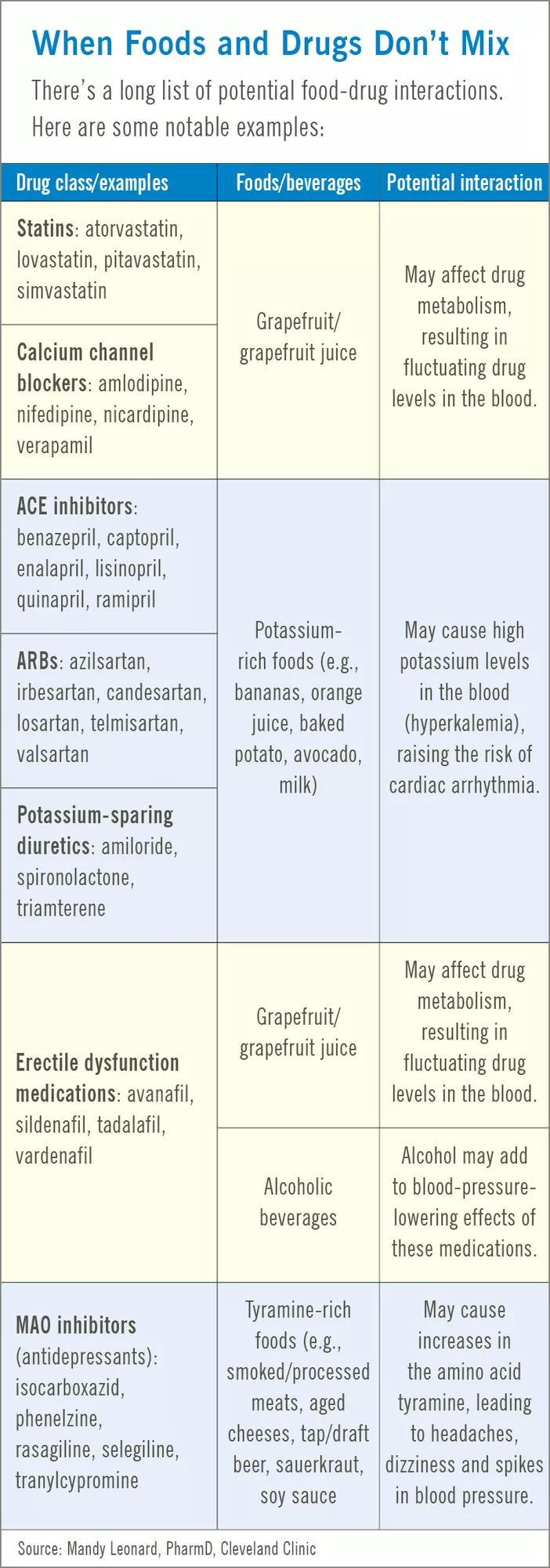
Hydrochlorothiazide, a common diuretic, can interact negatively with several medications. Careful monitoring and potential dosage adjustments are necessary when combining it with others.
Lithium
Avoid concurrent use with lithium. Hydrochlorothiazide can decrease lithium excretion, leading to elevated lithium levels and potential toxicity. Closely monitor lithium levels if combined use is unavoidable.
Digoxin
Hydrochlorothiazide can increase digoxin levels. This can increase your risk of digoxin toxicity. Regular monitoring of digoxin levels is essential if you take both medications.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Using NSAIDs (like ibuprofen or naproxen) alongside hydrochlorothiazide might reduce the diuretic effect of hydrochlorothiazide and potentially diminish its blood pressure-lowering effect. Inform your doctor about any NSAID use.
Potassium-Depleting Medications
- Amphotericin B Corticosteroids Carbenoxolone
These medications, combined with hydrochlorothiazide, can significantly increase your risk of hypokalemia (low potassium levels). Regular blood tests to monitor potassium levels are crucial.
Diabetes Medications
Hydrochlorothiazide may raise blood glucose levels, impacting the effectiveness of some diabetes medications (like insulin or oral hypoglycemics). Careful blood glucose monitoring and potential dosage adjustments are necessary.
Alcohol
Combining hydrochlorothiazide with alcohol can increase the risk of dehydration and orthostatic hypotension (dizziness upon standing). Limit alcohol consumption while taking hydrochlorothiazide.
Other Medications
Antihypertensives: Increased risk of low blood pressure. Muscle relaxants: Potential increased risk of muscle weakness.
This list isn’t exhaustive. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking to prevent potentially harmful interactions.