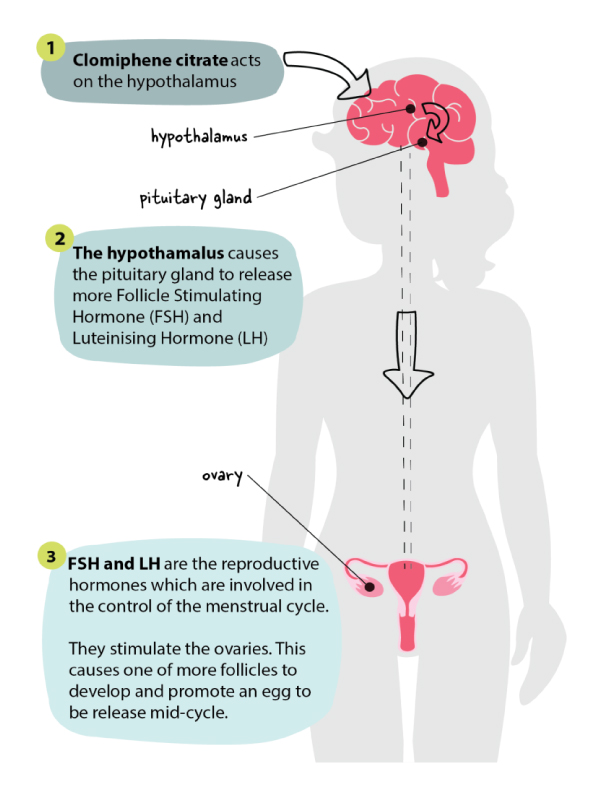
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, is a medication primarily used to stimulate ovulation in women. It works by blocking estrogen receptors in the brain, prompting the pituitary gland to release more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones are key to egg development and release.
Doctors prescribe Clomid for several reasons. Infertility due to ovulation disorders is a common application. Clomid can help women with irregular or absent periods conceive. It’s also sometimes used to treat anovulatory infertility, where the ovaries don’t release eggs.
Another use involves controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (COH) in conjunction with other fertility treatments like in-vitro fertilization (IVF). In this scenario, Clomid helps to mature multiple eggs, increasing the chances of successful fertilization.
However, it’s important to understand potential side effects. These can include hot flashes, headaches, mood swings, and ovarian enlargement. Multiple pregnancies are also possible, although rare. A doctor will carefully assess individual risk factors and benefits before prescribing.
| Ovulation induction in women with infertility | Blocks estrogen receptors, increasing FSH and LH release | Hot flashes, headaches, mood swings, ovarian enlargement |
| Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (COH) for IVF | Stimulates maturation of multiple eggs | Multiple pregnancies, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) |
Remember, Clomid is a prescription medication. Always consult your doctor before using it. They can determine if it’s the right treatment for you and monitor you for any potential complications.