Taking Lipitor without medical supervision increases your risk of experiencing adverse effects. Common side effects include muscle aches (myalgia), constipation, digestive upset, and headaches. Less common, but more serious, side effects involve liver problems, indicated by symptoms like jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) and dark urine. Rare but severe side effects include rhabdomyolysis, a breakdown of muscle tissue that can be life-threatening.
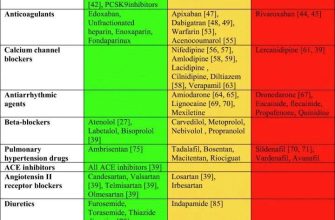
Lipitor interacts with various medications. Grapefruit juice significantly increases Lipitor’s concentration in your blood, potentially leading to dangerous side effects. Certain medications, including some antifungals, antibiotics, and medications for HIV/AIDS, can also interact negatively with Lipitor. Concomitant use of statins with fibrates, niacin, or cyclosporine may increase the risk of myopathy. Always inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking before starting Lipitor.
Muscle pain should be reported immediately to your doctor. Severe muscle pain or weakness could signal rhabdomyolysis, requiring prompt medical attention. Liver function tests may be needed to monitor for potential liver damage. Regular check-ups with your doctor are critical to monitor your cholesterol levels and adjust Lipitor dosage if necessary. Failure to do so significantly increases the risk of severe health complications.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting, stopping, or changing any medication, including Lipitor.