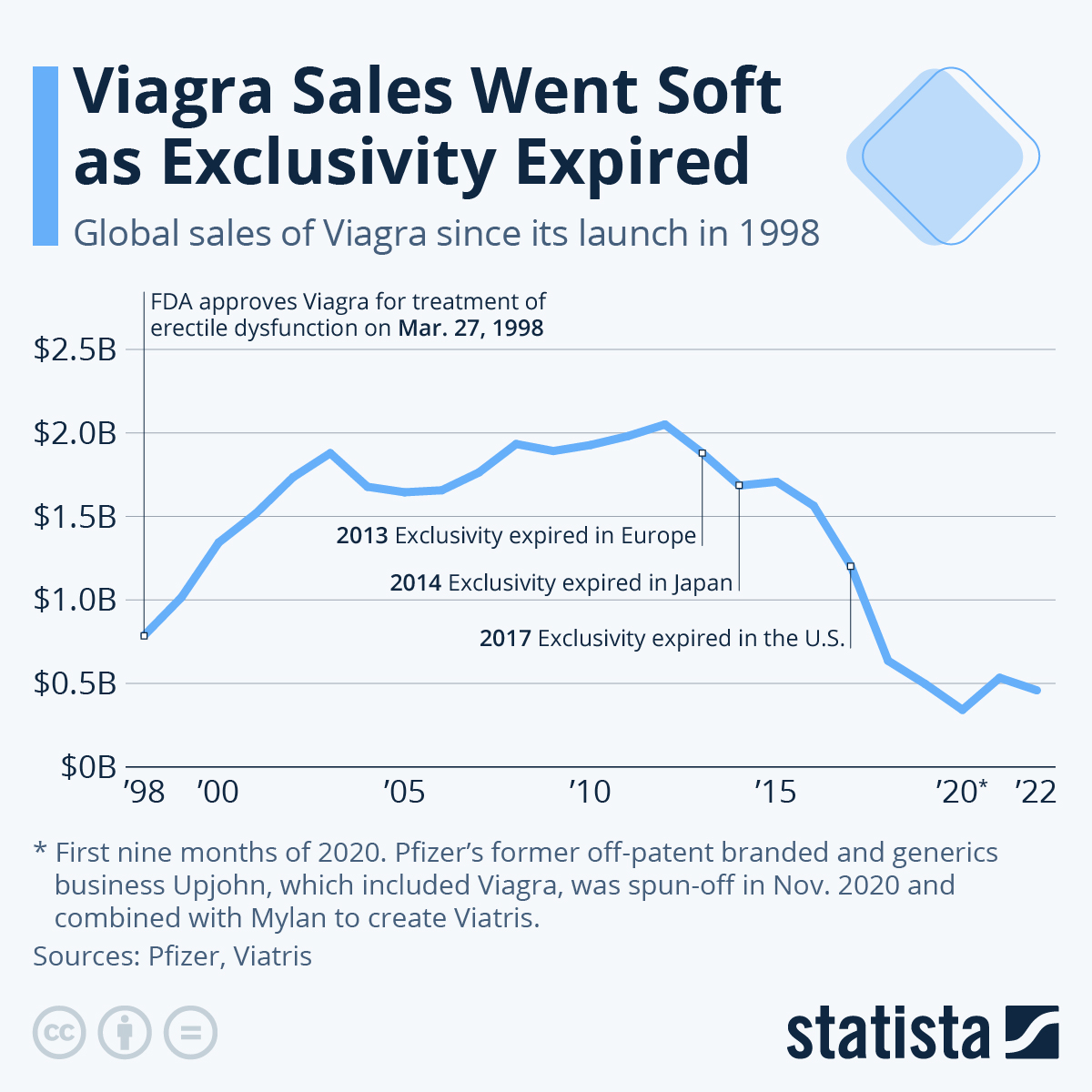
Pfizer’s Viagra sales peaked in 2008 at approximately $2 billion. Since then, sales have declined steadily due to patent expiration and increased generic competition. However, the drug still generates significant revenue for Pfizer.
Factors Affecting Sales
Several factors influence Viagra’s sales trajectory. The aging global population fuels demand, while the rise of generic alternatives significantly impacts pricing and market share. Direct-to-consumer advertising significantly impacted initial sales growth, though its effectiveness has lessened over time. Increased awareness of erectile dysfunction and improved healthcare access in developing nations present growth opportunities.
Strategic Implications for Pfizer
Pfizer actively mitigates declining Viagra sales through diversification. Investment in new erectile dysfunction treatments and expansion into related therapeutic areas, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia, reduces reliance on Viagra’s revenue. Strategic partnerships and licensing agreements also broaden Pfizer’s market reach and profitability. Pfizer’s continued focus on innovation remains key to its long-term financial health and sustained profitability beyond Viagra’s lifecycle. Data suggests a correlation between marketing spend and sales fluctuations, indicating the need for continuous strategic marketing efforts.
Future Projections
Predicting future Viagra sales requires considering several variables. Demographic shifts, competitive pressures, and the introduction of new therapies all play crucial roles. While a steady decline is anticipated, the persistent need for effective ED treatments suggests consistent, albeit reduced, sales for the foreseeable future. Precise figures remain challenging to project due to the dynamic nature of the pharmaceutical market.