Try Mupirocin Ointment. It’s a topical antibiotic, similar to Fucidin, effectively treating bacterial skin infections like impetigo and folliculitis. Mupirocin offers comparable efficacy with a proven track record.
Always consult a doctor before starting any new treatment. They can diagnose your specific condition and recommend the best course of action. This ensures safe and effective treatment tailored to your needs.
Several brands offer Mupirocin Ointment; compare prices and active ingredient concentrations before purchasing. Look for 2% mupirocin for optimal results. Remember to follow the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment carefully.
- Finding Effective Fucidin Alternatives in the USA
- Over-the-Counter Options
- Prescription Alternatives
- When to See a Doctor
- Important Note
- Alternative Treatments
- Identifying Your Skin Infection: When to Seek an Alternative to Fucidin
- Top 3 Over-the-Counter Fucidin Alternatives for Minor Skin Infections
- Important Considerations:
- Allergic Reactions:
- Prescription Options: Stronger Alternatives to Fucidin for Severe Infections
- Considering Systemic Antibiotics
- Choosing the Right Treatment
- Antibiotic Alternatives for Allergic Reactions
- Comparison of Antibiotic Potency
- Follow-up Care is Critical
- Natural Remedies and Home Care for Supporting Skin Healing (Alongside Medical Treatment)
- Dietary Adjustments
- Lifestyle Changes
- Additional Tips
- When to See a Doctor: Recognizing When an Alternative Isn’t Enough
Finding Effective Fucidin Alternatives in the USA
Consider Mupirocin ointment; it’s a topical antibiotic with a similar mechanism of action to Fucidin (fusidic acid).
Over-the-Counter Options
Bacitracin and Neosporin are readily available and treat minor skin infections. Check the active ingredients; they often combine bacitracin with neomycin and polymyxin B.
Prescription Alternatives
Retapamulin is another topical antibiotic your doctor might prescribe. It’s particularly useful for impetigo.
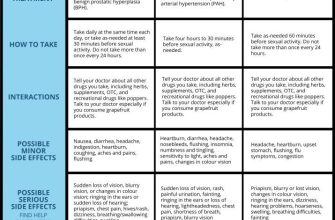
When to See a Doctor
Consult a physician if your infection worsens, spreads, or doesn’t improve after a few days of self-treatment. They can diagnose the specific infection and prescribe the right medication, perhaps a stronger antibiotic or antifungal depending on the cause.
Important Note
Always follow the instructions on the medication label carefully. Never use antibiotics without a proper diagnosis. Incorrect usage can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Alternative Treatments
For minor skin irritations, tea tree oil or aloe vera gel can provide soothing relief. However, they are not substitutes for antibiotics in treating bacterial infections.
Identifying Your Skin Infection: When to Seek an Alternative to Fucidin
Notice persistent redness, swelling, or pus? See your doctor. Fucidin might not be suitable for all skin infections.
Bacterial infections: Fucidin targets Staphylococcus aureus. If your infection involves other bacteria (like Streptococcus), another antibiotic is needed. Your doctor can perform a swab test for accurate identification.
Fungal infections: Fucidin is ineffective against fungi. Ringworm, athlete’s foot, and yeast infections require antifungal treatments. These are easily distinguishable by their characteristic appearances and locations.
Viral infections: Cold sores and chicken pox are viral, not bacterial. Fucidin won’t help; antiviral medication is necessary.
Severe infections: Extensive skin infections, those accompanied by fever, or spreading rapidly require immediate medical attention. Delaying treatment can worsen the condition.
Allergic reactions: Experience itching, rash, or swelling after applying Fucidin? Stop use immediately and consult a doctor. Alternatives with different active ingredients are available.
Ineffective treatment: If symptoms don’t improve after several days of using Fucidin, consult your doctor. The infection may require a stronger or different antibiotic.
Remember: This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment of skin infections.
Top 3 Over-the-Counter Fucidin Alternatives for Minor Skin Infections
For minor skin infections, consider these readily available options:
- Mupirocin Ointment (Bactroban): This antibiotic ointment effectively targets bacterial skin infections like impetigo and folliculitis. Apply a thin layer to the affected area three times daily, as directed on the label. Always wash your hands before and after application.
- Bacitracin Ointment: A common topical antibiotic, bacitracin combats many bacterial infections. Apply a thin layer to the affected area several times a day. This ointment is often combined with neomycin and polymyxin B in triple antibiotic ointments, offering broader coverage.
- Benzoyl Peroxide Cream/Gel: While primarily known for acne treatment, benzoyl peroxide’s antibacterial properties make it suitable for certain minor skin infections, particularly those with mild inflammation. Apply as directed on the product label. Start with a low concentration and increase gradually if needed. Remember to always follow the instructions carefully.
Important Considerations:
- Always read and follow the instructions on the product label.
- If symptoms worsen or persist for more than a week, consult a doctor.
- These alternatives may not be suitable for all types of skin infections. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the best course of treatment.
Allergic Reactions:
Be aware of potential allergic reactions. Stop use and seek medical attention if you experience redness, swelling, itching, or other unusual symptoms.
Prescription Options: Stronger Alternatives to Fucidin for Severe Infections
For severe skin infections unresponsive to Fucidin, your doctor might prescribe a stronger antibiotic like clindamycin or erythromycin. These offer broader antibacterial coverage.
Considering Systemic Antibiotics
If the infection is widespread or shows signs of systemic involvement (fever, lymphadenopathy), intravenous antibiotics such as vancomycin or linezolid may be necessary. These are administered in a hospital setting.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The choice of antibiotic depends on several factors: the specific bacteria causing the infection (determined by culture and sensitivity testing), the severity of the infection, and your overall health. Always follow your doctor’s instructions for dosage and duration of treatment.
Antibiotic Alternatives for Allergic Reactions
If you have an allergy to penicillin or its derivatives, your doctor will prescribe alternative antibiotics. This might include tetracyclines or macrolides, depending on the infection’s nature.
Comparison of Antibiotic Potency
| Antibiotic | Spectrum of Activity | Administration Route | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clindamycin | Gram-positive and some anaerobic bacteria | Oral, topical, intravenous | Skin infections, bone infections |
| Erythromycin | Gram-positive bacteria | Oral, topical | Skin infections, respiratory tract infections |
| Vancomycin | Gram-positive bacteria (including MRSA) | Intravenous | Severe skin infections, bloodstream infections |
| Linezolid | Gram-positive bacteria (including MRSA and VRE) | Oral, intravenous | Severe skin infections, pneumonia |
Follow-up Care is Critical
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor your progress and ensure the infection is completely cleared. Contact your doctor immediately if your symptoms worsen or don’t improve.
Natural Remedies and Home Care for Supporting Skin Healing (Alongside Medical Treatment)
Apply a cool compress of chamomile tea to soothe inflammation and reduce discomfort. Chamomile’s anti-inflammatory properties can help calm irritated skin.
Maintain a clean and dry environment. Gently pat the affected area dry after cleansing to prevent further irritation. Avoid harsh scrubbing.
Dietary Adjustments
Increase your intake of Vitamin C-rich foods like citrus fruits and berries. Vitamin C aids collagen production, crucial for skin repair.
Consume foods high in zinc, such as nuts and seeds. Zinc supports the immune system and promotes wound healing.
Lifestyle Changes
Minimize sun exposure. UV rays can hinder healing and increase the risk of scarring. Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher when outdoors.
Ensure adequate hydration by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Proper hydration supports overall skin health.
Additional Tips
Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers. Harsh chemicals can irritate already sensitive skin.
Avoid scratching or picking at the affected area. This can worsen the condition and lead to scarring.
Always consult your doctor before starting any new treatment, including natural remedies, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
When to See a Doctor: Recognizing When an Alternative Isn’t Enough
If your skin infection shows no improvement after three days of using an alternative treatment, see a doctor. This is especially true if the infection worsens or spreads.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience fever, chills, swollen lymph nodes, or red streaks emanating from the infected area. These could indicate a serious infection requiring antibiotics.
Deep wounds, puncture wounds, or animal bites demand professional medical evaluation, regardless of any alternative treatments. These wounds are prone to infection and require specialized care.
Diabetic patients should contact their doctor about any skin infection, no matter how minor. Diabetics have a higher risk of serious complications.
Children under two years old with skin infections require immediate medical attention. Their immune systems are less developed, increasing the risk of severe complications.
If you have a weakened immune system due to illness or medication, consult a doctor before using any alternative treatment and seek professional care for any skin infection.
Persistent pain, significant swelling, or pus discharge also necessitate a visit to your doctor. These signs suggest the infection requires stronger intervention.
Allergic reactions, such as itching, rash, or difficulty breathing, after using an alternative treatment require immediate medical attention. Stop using the alternative and seek help immediately.