Try Diflucan (fluconazole)! This prescription medication effectively targets a wide range of fungal infections, offering rapid symptom relief. Experience the difference: Diflucan’s powerful formula works quickly to reduce discomfort and promote healing.
Diflucan combats various fungal infections, including vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and certain skin infections. Its single-dose option provides convenience for specific infections, while longer treatment courses address more complex cases. Speak to your doctor about the best treatment plan for you.
Don’t suffer unnecessarily. Diflucan provides a targeted solution, allowing you to reclaim your health and well-being. Consult your healthcare provider to determine if Diflucan is the right choice for your specific fungal infection. They can assess your individual needs and provide personalized advice.
- Diflucan (Fluconazole): Your Guide to Effective Yeast Infection Treatment
- Understanding Your Treatment
- Dosage and Administration
- Possible Side Effects & Precautions
- Maintaining Vaginal Health
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Understanding and Identifying Yeast Infections: Recognizing the Symptoms
- Recognizing Less Common Symptoms
- When to See a Doctor
- Important Considerations
- Diflucan Dosage and Treatment Regimen: A Simple Explanation
- Managing Yeast Infection Recurrences: Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
- Diflucan vs. Over-the-Counter Treatments: When to See a Doctor
Diflucan (Fluconazole): Your Guide to Effective Yeast Infection Treatment
Treat your yeast infection quickly and reliably with Diflucan (fluconazole). This single-dose oral medication targets the Candida fungus responsible for most vaginal yeast infections. For many, relief begins within 24-48 hours.
Understanding Your Treatment
Diflucan works by inhibiting the growth of the fungus, thereby allowing your body to naturally clear the infection. Complete the prescribed course, even if symptoms improve quickly, to prevent recurrence.
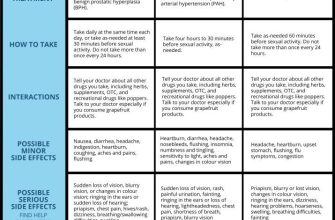
Dosage and Administration
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and the severity of the infection. Follow their instructions meticulously regarding frequency and duration of treatment. Common dosages include a single 150 mg tablet or a course of multiple smaller doses.
Possible Side Effects & Precautions
| Side Effect | Frequency | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Headache | Common | Drink plenty of water; consider over-the-counter pain relief. |
| Nausea | Common | Take Diflucan with food. |
| Abdominal pain | Less common | Contact your doctor. |
| Rash | Rare | Stop taking Diflucan and seek immediate medical attention. |
Inform your doctor about any pre-existing medical conditions, including liver problems or allergies, before starting treatment. Diflucan may interact with other medications; ensure your doctor is aware of all medications you are taking.
Maintaining Vaginal Health
After treatment, maintain good hygiene practices to prevent future infections. Avoid tight-fitting clothing and use breathable fabrics. Consider probiotics to support a healthy vaginal microbiome.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe side effects, the infection worsens, or symptoms persist after completing treatment.
Understanding and Identifying Yeast Infections: Recognizing the Symptoms
Yeast infections, primarily caused by Candida, manifest differently depending on location. Vaginal yeast infections present with intense itching, thick white discharge resembling cottage cheese, and soreness. Penile yeast infections cause redness, itching, and a white coating on the penis. Oral thrush, a yeast infection in the mouth, creates creamy white patches on the tongue and inner cheeks, often accompanied by soreness.
Recognizing Less Common Symptoms
Beyond the typical symptoms, consider less common indicators. For vaginal infections, pain during urination or intercourse is possible. Oral thrush may lead to difficulty swallowing. Skin yeast infections, often appearing in skin folds, present as bright red rashes, scaling, and intense itching. Systemic candidiasis, a severe, widespread infection, displays flu-like symptoms: fever, chills, and fatigue. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience systemic symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a doctor if: Your symptoms are severe; home remedies prove ineffective; you experience unusual symptoms; you suspect a systemic infection; or you have recurring infections. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing yeast infections effectively. Accurate diagnosis ensures the correct treatment plan, preventing further complications.
Important Considerations
Proper hygiene practices help prevent yeast infections. Maintaining a dry environment, especially in skin folds and the genital area, is beneficial. Avoid tight-fitting clothing, which traps moisture. A balanced diet can also contribute to overall health and potentially reduce infection risk. While over-the-counter treatments are available, always follow instructions carefully.
Diflucan Dosage and Treatment Regimen: A Simple Explanation
Dosage depends entirely on your specific infection and your doctor’s prescription. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor.
Yeast Infections (Vaginal Candidiasis): A single 150 mg oral dose is often sufficient. Some cases may require a 7-day course of 150 mg daily.
Oral Thrush (Oral Candidiasis): Treatment typically involves a 100-150 mg daily dose for 7-14 days. Your doctor determines the exact duration.
Cryptococcal Meningitis: This serious infection necessitates a higher dose, usually starting at 400 mg daily, adjusted based on your response and blood tests. This requires close medical supervision.
Coccidioidomycosis: Treatment duration varies greatly depending on severity, ranging from several weeks to months. The prescribed dosage will be determined by your physician, often beginning with a higher dose.
Other Fungal Infections: Dosage and duration vary considerably depending on the specific fungus and its location in the body. Your doctor will tailor the treatment to your unique needs. They will monitor your progress using blood tests and clinical assessments.
Remember: This information is for general understanding only. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. They will consider your medical history, current health status, and the nature of your infection when determining the most appropriate Diflucan dosage and treatment plan.
Potential Side Effects: Common side effects include nausea, headache, and diarrhea. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience serious side effects such as severe allergic reactions or liver problems.
Managing Yeast Infection Recurrences: Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Maintain a healthy vaginal pH. Use unscented, hypoallergenic soaps and avoid douching; these disrupt the natural balance.
Wear breathable cotton underwear. Synthetic fabrics trap moisture, creating a favorable environment for yeast growth.
- Choose loose-fitting clothing to improve air circulation.
- Change out of damp clothing promptly after exercise or sweating.
Control blood sugar levels. High blood sugar can increase yeast infection risk. If you have diabetes, work closely with your doctor to manage your condition.
- Eat a balanced diet low in refined sugars and processed foods.
- Monitor your blood glucose regularly if diabetic.
Strengthen your immune system. A weakened immune system makes you more susceptible to infections. Consider these strategies:
- Prioritize sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly.
- Manage stress effectively: Practice relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
- Eat a nutrient-rich diet: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Practice good hygiene. Wipe from front to back after using the restroom to prevent fecal bacteria from entering the vagina.
Limit refined sugar intake. Yeast thrives on sugar. Reduce consumption of sugary drinks, candy, and processed foods.
Stay hydrated. Adequate hydration supports overall health and can aid in preventing yeast infections.
If infections persist despite these changes, consult your doctor. They can help determine underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatment.
Diflucan vs. Over-the-Counter Treatments: When to See a Doctor
Choose Diflucan for severe or persistent yeast infections. Over-the-counter (OTC) creams treat mild, superficial infections. If your symptoms are severe–intense itching, burning, swelling, or if the infection spreads–consult a doctor immediately. Diflucan is a prescription antifungal medication, more potent than OTC options.
Consider OTC treatments for mild symptoms. Many vaginal yeast infections respond well to OTC antifungal creams like miconazole or clotrimazole. These are available without a prescription and offer localized relief. However, use them for no more than three days without improvement.
Seek medical attention if symptoms persist. If OTC treatments fail to relieve symptoms after three days, or if symptoms return within two weeks, schedule a doctor’s appointment. Underlying conditions or a resistant infection might require stronger medication or a different treatment approach.
Diflucan is a targeted solution. While OTC options treat surface symptoms, Diflucan tackles the infection systemically, reaching areas OTC treatments may miss. This makes it more effective for severe or recurring infections.
Note: This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication.