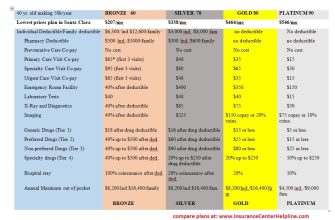
Metformin primarily treats type 2 diabetes. It helps your body respond better to insulin and reduces the amount of sugar your liver produces. Doctors prescribe it to lower blood sugar levels, preventing long-term complications like heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve problems. Dosage depends on individual needs and is adjusted accordingly.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Beyond diabetes, metformin often helps women with PCOS. PCOS causes hormonal imbalances, leading to irregular periods, acne, and weight gain. Metformin improves insulin sensitivity, potentially regulating periods and reducing symptoms. However, it’s not a cure-all and may not work for everyone.
Other Potential Uses
Research explores metformin’s potential in other areas. Some studies suggest it might aid in cancer prevention, specifically certain types. Preliminary data indicates possible benefits in slowing cancer growth. More research is needed to confirm these findings and determine appropriate applications.
Metformin Dosage: A General Guideline
| Type 2 Diabetes | 500 mg once daily | 2550 mg |
| PCOS | 500 mg once daily | 2000 mg |
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or changing any medication.
Important Considerations
Metformin can cause side effects, including nausea, diarrhea, and stomach upset. These are often mild and improve over time. Rarely, more serious side effects can occur. Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial for monitoring your health and adjusting your dosage as needed. Proper diet and exercise alongside metformin are vital for managing diabetes and PCOS effectively.