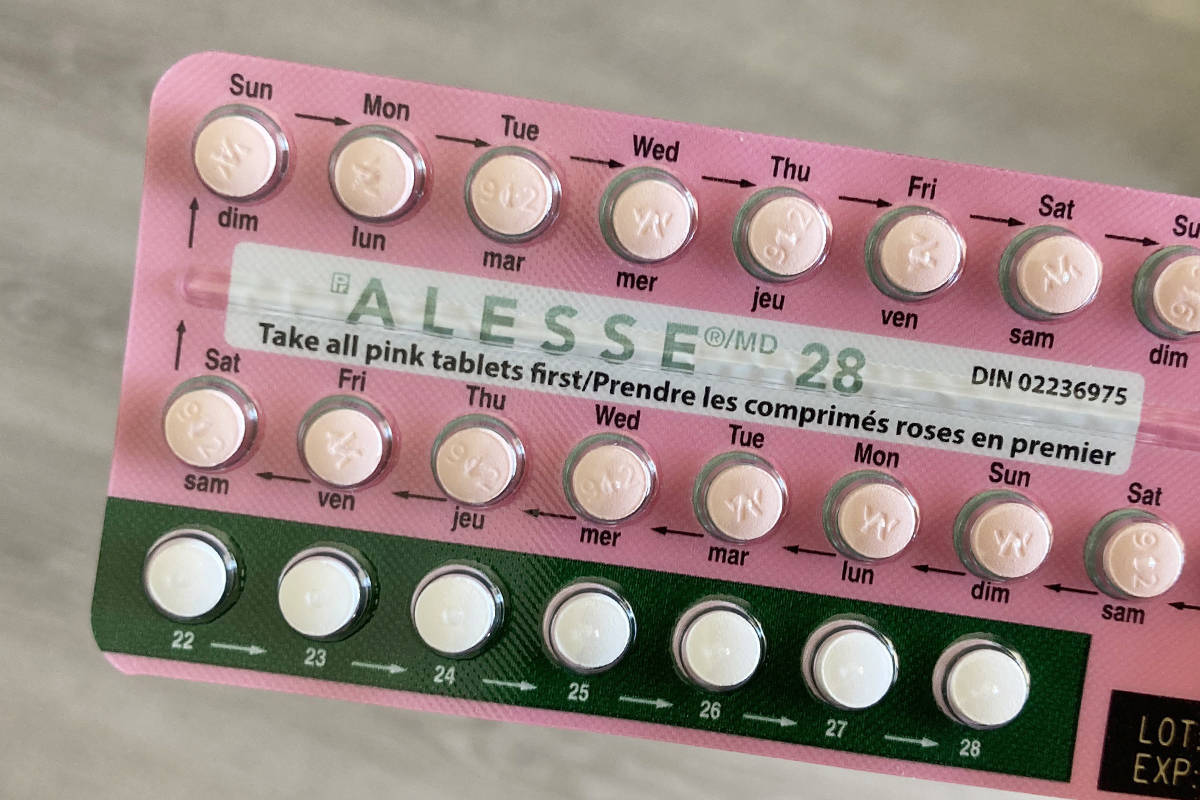
Alesse is a combined oral contraceptive pill containing ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel. It prevents pregnancy by suppressing ovulation.
Understanding Alesse
Alesse comes in different strengths, so it’s crucial to follow your doctor’s prescription precisely. Remember consistent daily use is key to its effectiveness. Missed pills can reduce its efficacy; refer to the patient information leaflet for advice on managing missed pills.
Common side effects include changes in menstrual bleeding (like spotting or heavier periods), breast tenderness, and nausea. These usually subside after a few months. Serious side effects are rare but warrant immediate medical attention. These include severe abdominal pain, chest pain, or shortness of breath.
Alesse and Your Health
Alesse may not be suitable for everyone. Women with certain health conditions, like blood clots, high blood pressure, or a history of migraines with aura, should discuss its use with their doctor. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are recommended while taking Alesse.
- Consult your physician: Before starting Alesse, discuss your medical history and any medications you’re currently taking. Regular check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor to monitor your health and the effectiveness of Alesse. Report side effects: Immediately report any unusual or concerning side effects to your doctor.
Alternative Contraceptives
If Alesse isn’t right for you, there are many other contraceptive options. Your doctor can help you find the best method for your individual needs and lifestyle. This might include other hormonal contraceptives, IUDs, or barrier methods like condoms.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions about your health or treatment.